search
What is Digital Surface ModelïŒDSMïŒ
Apr 18, 2023
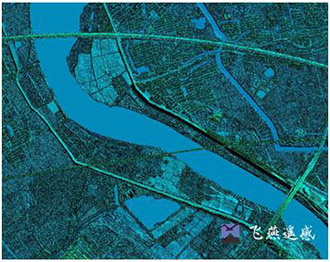
In a LiDAR system, a light pulse travels to the ground, and when the light pulse bounces off its target and returns to the sensor, the detection range is obtained. LiDAR provides massive point clouds with elevation values, which can come from building tops, tree canopies, power lines, and other features, and DSM captures natural and architectural features on the Earth's surface.
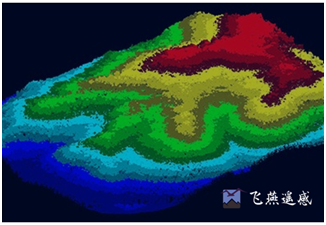
DSM can be used for 3D modeling in telecommunications, urban planning and aviation. In aviation, DSM can determine runway obstacles in the approach area. In vegetation management, DSM can see the location and amount of vegetation encroachment. DSM can be used in urban planning to check whether proposed buildings will interfere with views.
-
 Jan 10, 2023
Jan 10, 2023What is Satellite Acquisition?
Satellite acquisition refers to the process of finding and locking onto a satellite signal for the purpose of receiving and transmitting data. More > -
 Apr 12, 2023
Apr 12, 2023The Difference Between DOM and DSM
Digital Orthophoto Map (DOM) has the advantages of high precision, rich information, intuitive and realistic, fast acquisition, etc., and can be used as map analysis background control information. More > -
 Apr 19, 2023
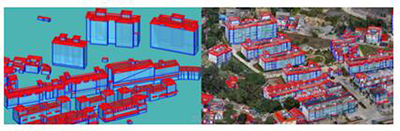
Apr 19, 2023Real-Scene 3D White Model Construction with Multi-Source Data Fusion
As the initial product of the 3D architectural model, the white model contains information such as the location, height, shape, area, and volume of the building More > -
 May 17, 2023
May 17, 2023Features of Oblique Photography
The birth of oblique photography technology has subverted the traditional way of operation. More > -
 Jul 03, 2023
Jul 03, 2023What is Digital Surface Model
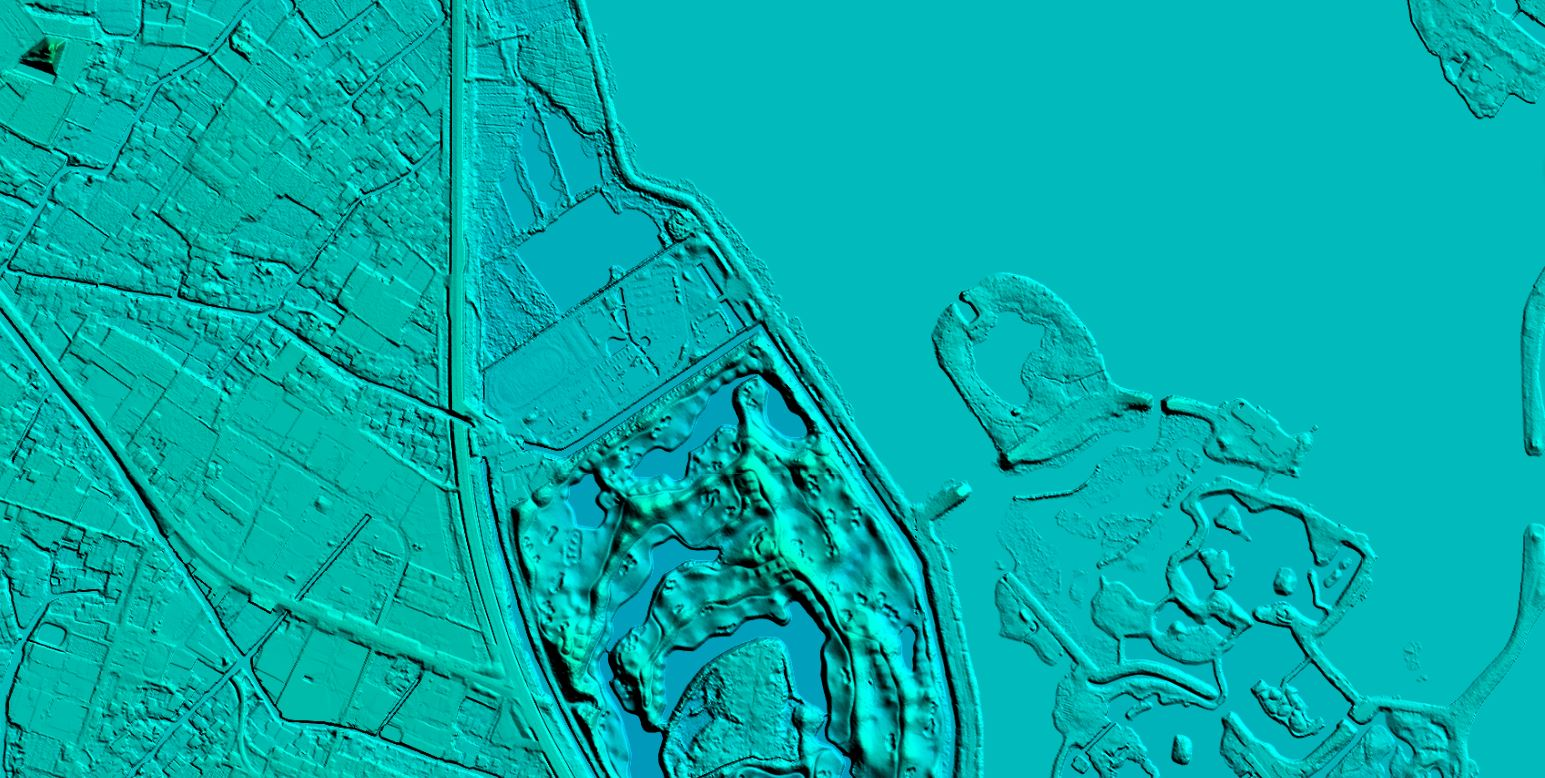
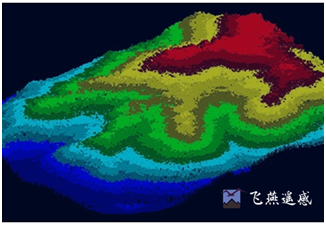
Digital Surface Model (DSM) refers to a ground elevation model that includes the heights of surface buildings, bridges and trees. Compared with DEM, DEM only contains the elevation information of the terrain and does not include other surface information. DSM is based on DEM and further covers the elevation of other surface information except the ground. In some areas where there is a demand for building height, it has received a lot of attention. More >
 AIMS
AIMS AIMS-H Long Focus
AIMS-H Long Focus Farsightâą System
Farsightâą System Riegl VQ-1560i
Riegl VQ-1560i Riegl VQ-780II
Riegl VQ-780II UltraCam Eagle M3
UltraCam Eagle M3 Y-1 VTOL UAV
Y-1 VTOL UAV Aerial Acquisition
Aerial Acquisition UAV Acquisition
UAV Acquisition Satellite Acquisition
Satellite Acquisition Field Acquisition
Field Acquisition Integrated
Integrated LiDAR
LiDAR Orthophoto
Orthophoto DEM
DEM DTM/DSM
DTM/DSM 3D Mapping
3D Mapping Topographic
Topographic Infrared
Infrared Feature Extraction
Feature Extraction BIM
BIM Transportation
Transportation Water
Water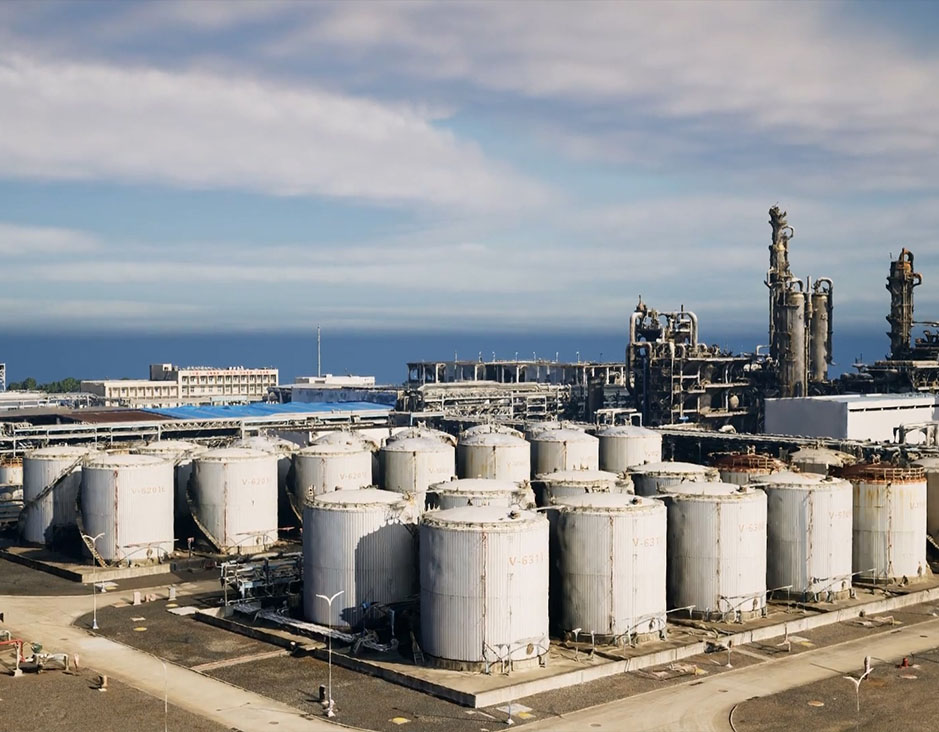 power
power 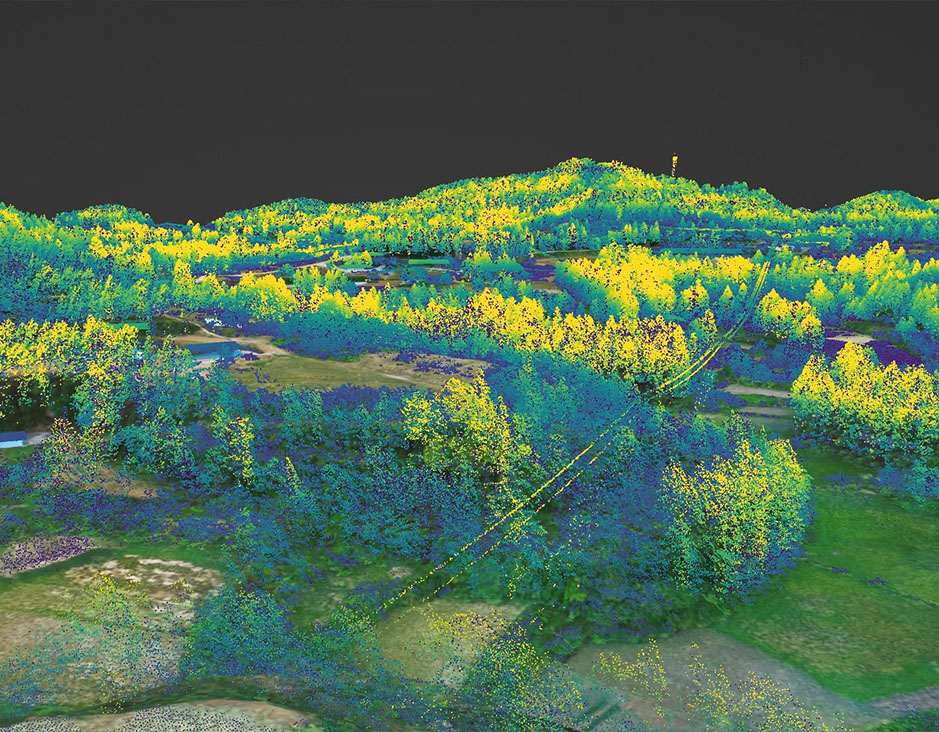 Forestry
Forestry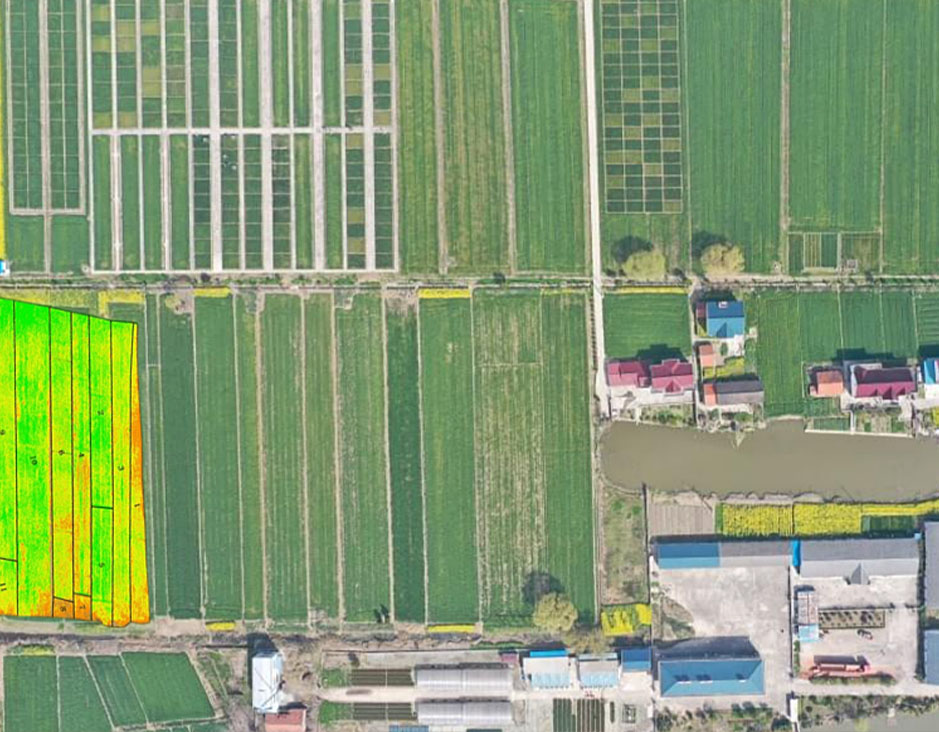 Agriculture
Agriculture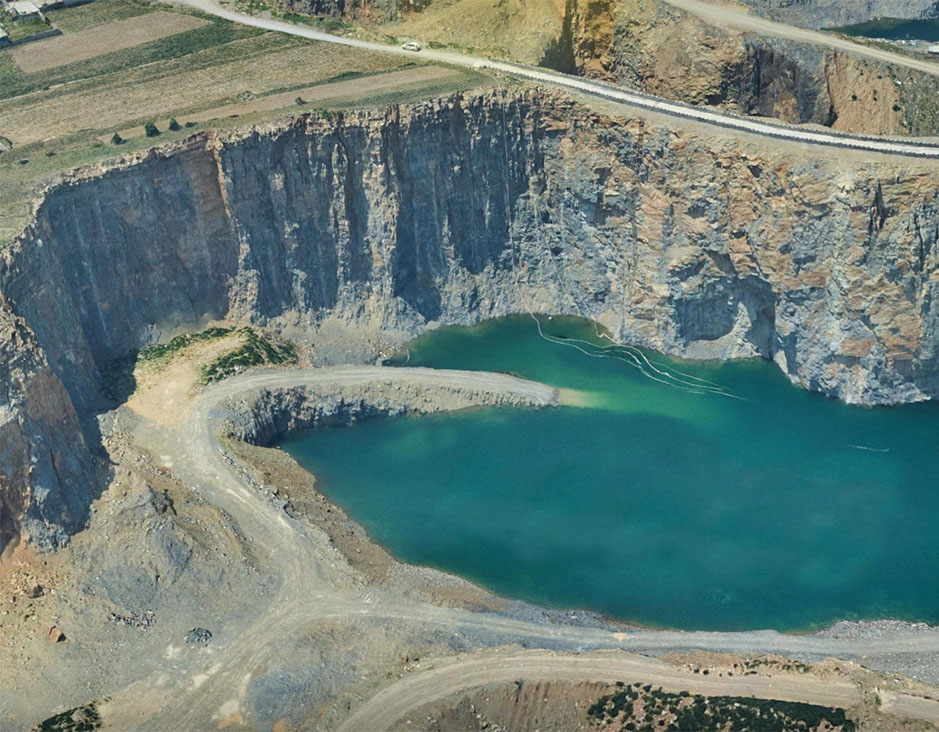 Mines & Quarries
Mines & Quarries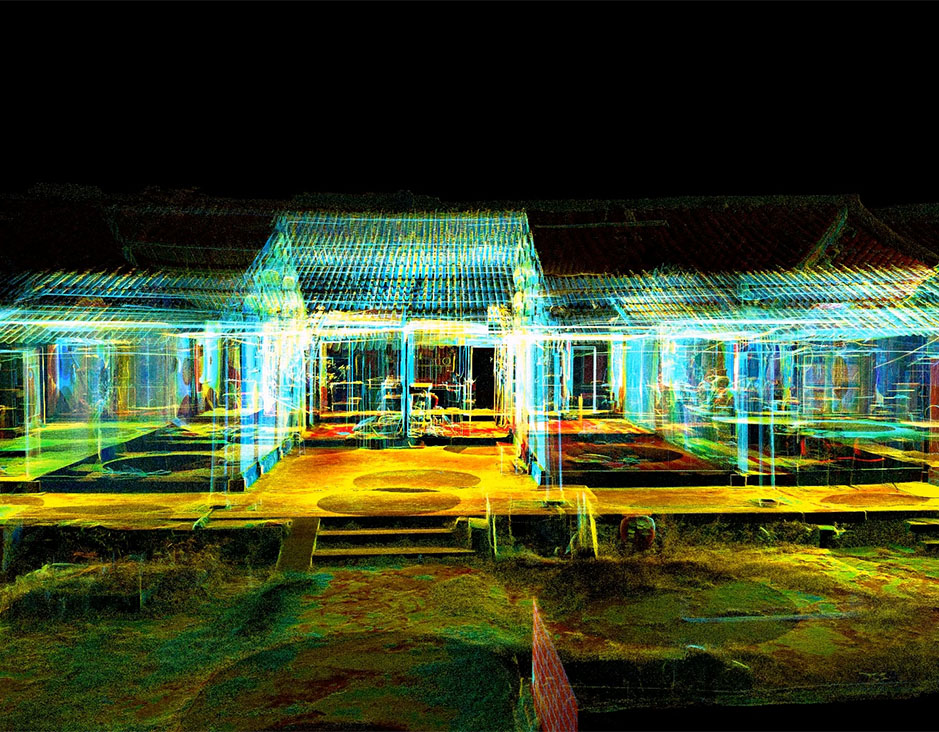 Heritage Buildings
Heritage Buildings About feiyan
About feiyan Recognition
Recognition Cases
Cases