search
How to build DEM
Jun 30, 2023

There are many ways to build DEM, classified from the way of data acquisition:
1) Measure directly from the ground. The instruments involved include components such as horizontal guide rails, styli, stylus holders, and relative elevation measurement boards. High-end instruments such as GPS, total station, and field measurement can also be used;
2) According to aerial or aerospace images, it is obtained through photogrammetry, such as three-dimensional coordinate instrument observation and aerothree encryption method, analytical mapping, digital photogrammetry, etc.;
3) Acquisition from the existing topographic map, such as grid reading method, digitizer hand-held tracking and scanner semi-automatic acquisition and then generate DEM through interpolation.
There are many DEM interpolation methods, mainly including overall interpolation, block interpolation and point-by-point interpolation:
1) The fitting model of overall interpolation is established by the observation values of all sampling points in the study area;
2) Block interpolation is to divide the reference space into several blocks of the same size, and use different functions for each block;
3) Point-by-point interpolation is centered on the point to be inserted, defining a local function to fit the surrounding data points. The range of data points changes with the position to be inserted, so it is also called moving fitting method.

-
 Jul 30, 2021
Jul 30, 2021The DEM (1:1000) 12000kmÂČ of the entire watershed area was obtained and processed within 40 days.
Torrential rains have battered Zhengzhou and its surrounding area during the last ten days, displacing hundreds of thousands of people and causing 1.22 billion yuan of economic damage, Henan authorities said Thursday. More > -
 Mar 22, 2022
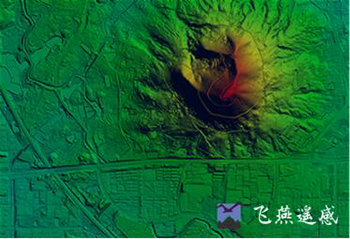
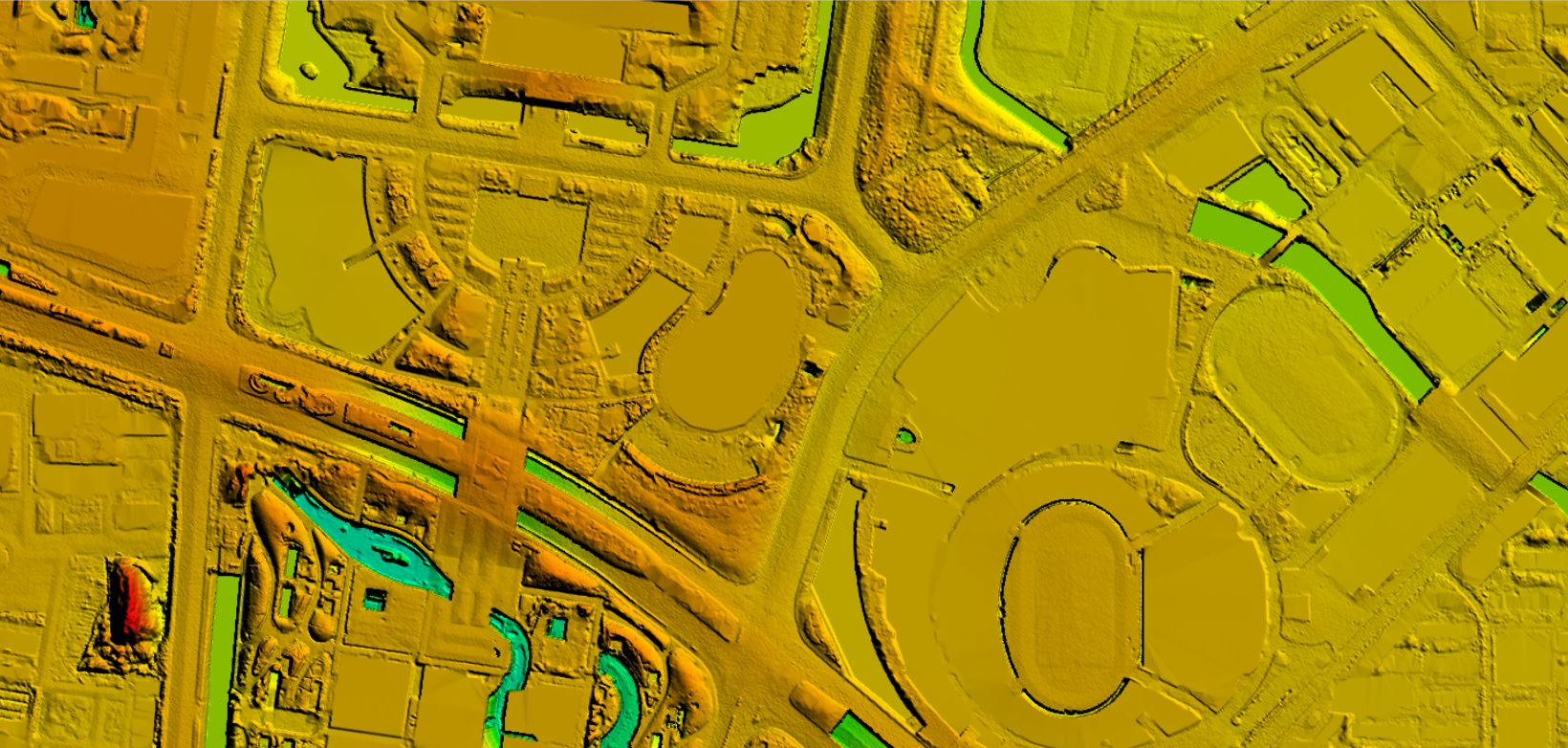
Mar 22, 2022Guangxi Forestry Bureau's DEM
After collecting the data, the processing of the point cloud data will be done to obtain the desired outputs. In this process, filtering and classification algorithms will be used to remove noise from the data to obtain a clean point cloud. More > -
 Sep 26, 2022
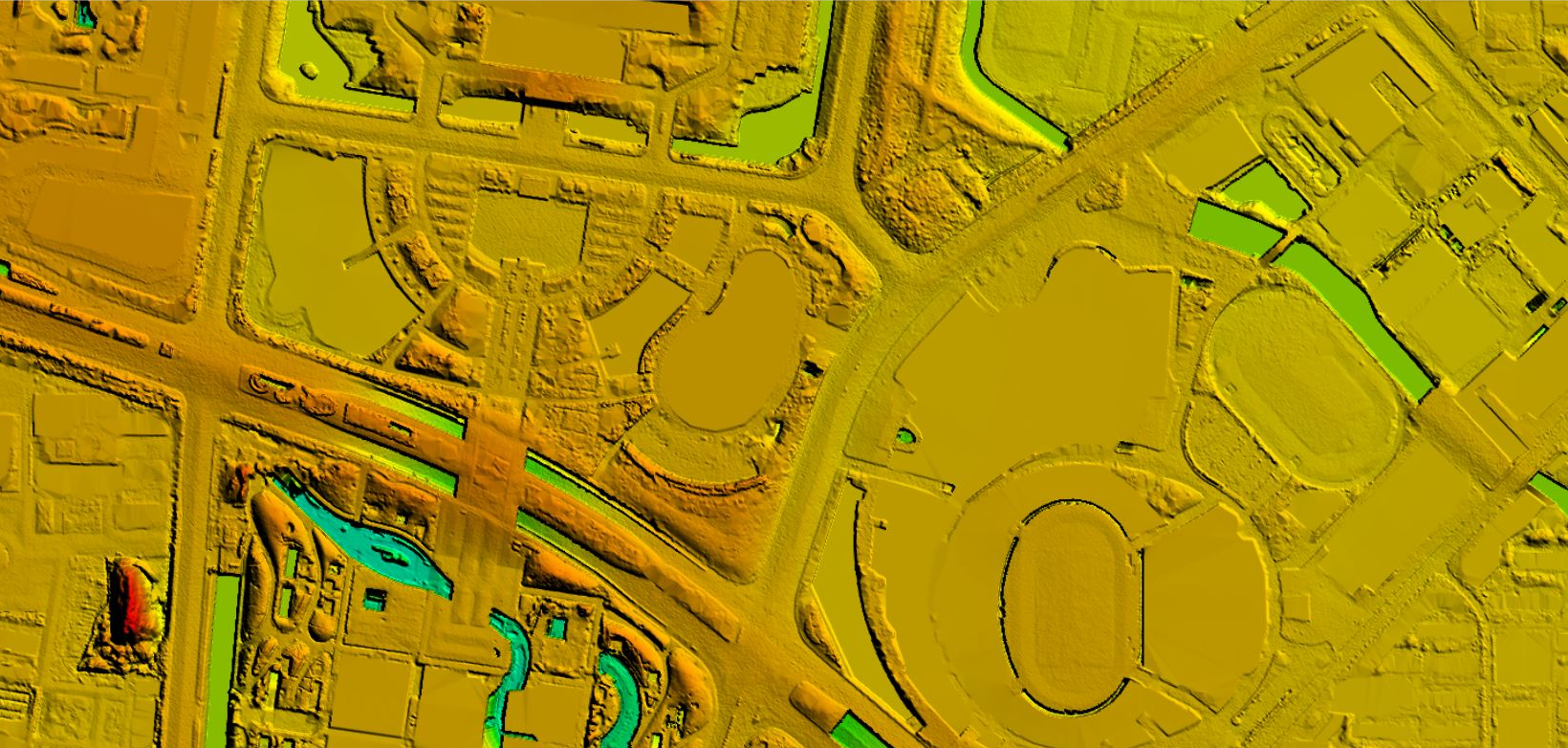
Sep 26, 2022DEM Editing In DOM Aerial Triangulation
DEM editing is an indispensable part of producing orthophotos(DOM). More > -
 Apr 07, 2023
Apr 07, 2023What is Digital Elevation ModelïŒDEMïŒïŒ
A digital elevation model (DEM) is a digital representation of the topography of a geographic area. More > -
 Apr 10, 2023
Apr 10, 2023Application of Digital Elevation Model (DEM) in Natural Resources Field
There are many applications of Digital Elevation Model (DEM) in natural resources field, such as environmental analysis, forest management, etc. More > -
 Apr 11, 2023
Apr 11, 2023Application of Digital Elevation Model (DEM) in Multiple Fields
âDigital elevation model is an important type of geographic data used to represent the topography of a geographic area in a numerical format. More > -
 Apr 20, 2023
Apr 20, 2023What is Digital Elevation Model(DEM)
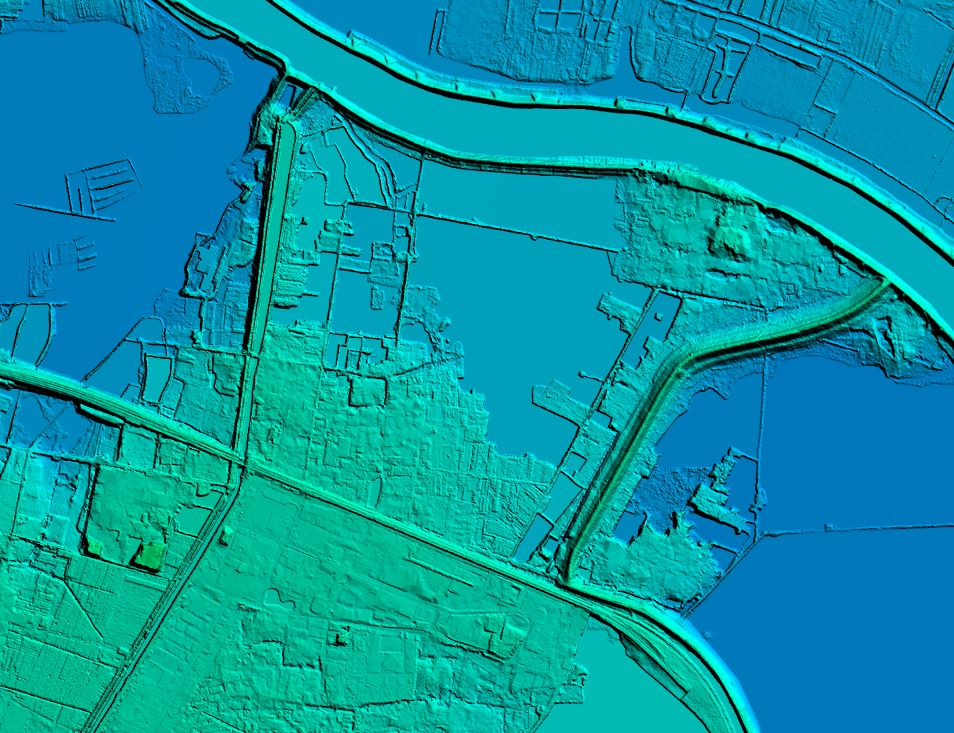
The Digital Elevation Model is a bare earth raster grid referenced to a vertical datum, and when non-ground points such as bridges and roads are filtered out, a smooth digital elevation model is obtained. More > -
 Apr 26, 2023
Apr 26, 2023What is 4D?
4D technology: Digital Elevation Model (DEM), Digital Orthophoto (DOM), Digital Line Drawing (DLG) and Digital Raster Map (DRG). More > -
 Jul 04, 2023
Jul 04, 2023What are the uses of Digital Elevation Model
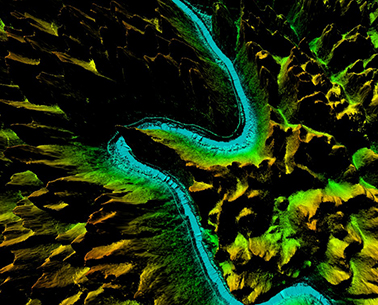
Digital Elevation Model is a data set of plane coordinates (X, Y) and elevation (Z) of regular grid points within a certain range. It mainly describes the spatial distribution of regional geomorphology, and uses contour lines or similar three-dimensional models for data collection. Acquisition (including sampling and measurement), followed by data interpolation. More >
 AIMS
AIMS AIMS-H Long Focus
AIMS-H Long Focus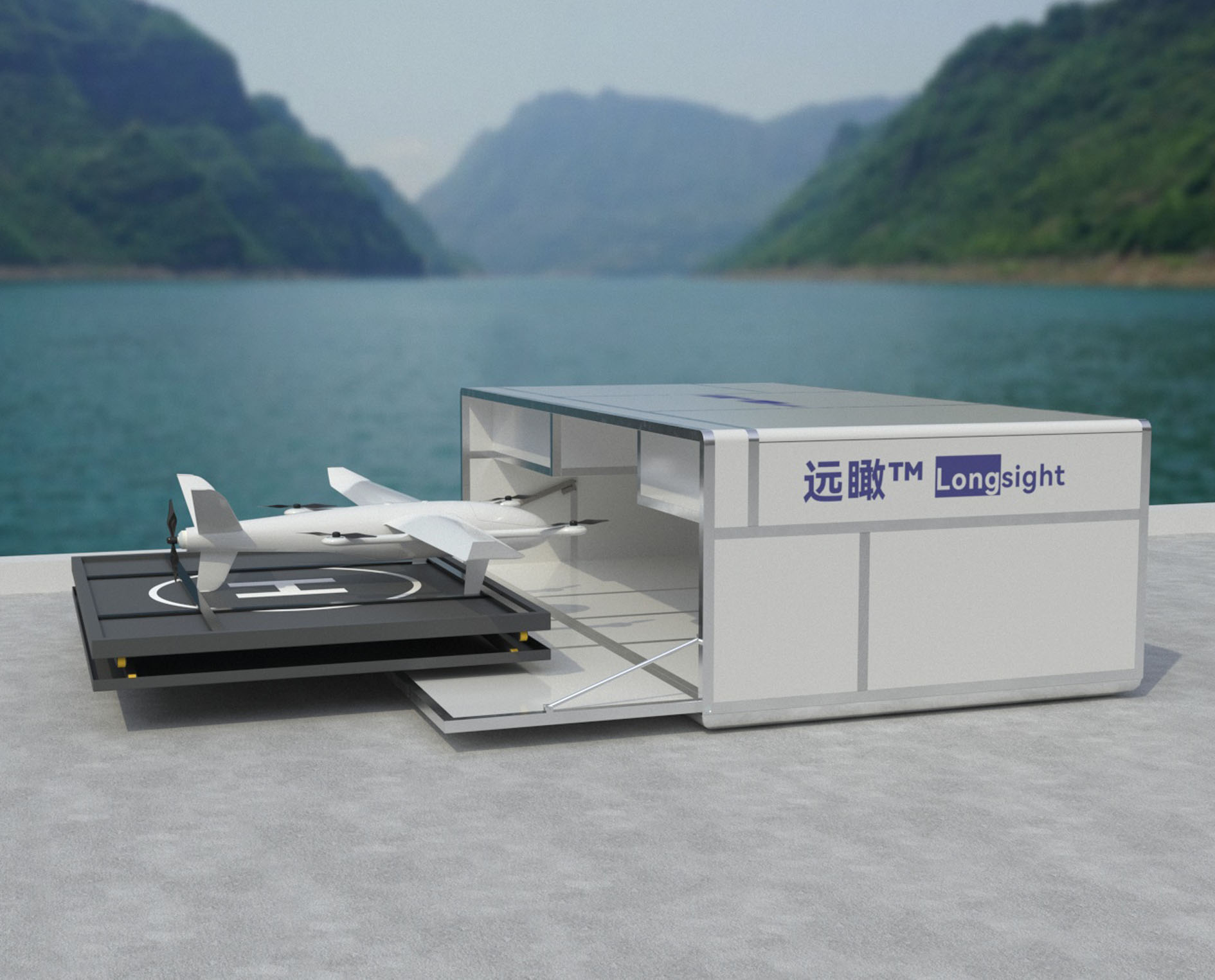 Farsightâą System
Farsightâą System Riegl VQ-1560i
Riegl VQ-1560i Riegl VQ-780II
Riegl VQ-780II UltraCam Eagle M3
UltraCam Eagle M3 Y-1 VTOL UAV
Y-1 VTOL UAV Aerial Acquisition
Aerial Acquisition UAV Acquisition
UAV Acquisition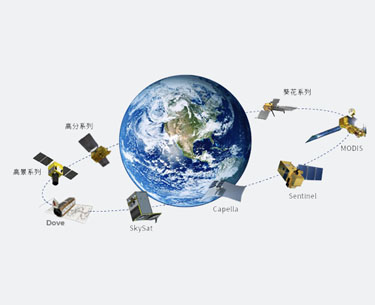 Satellite Acquisition
Satellite Acquisition Field Acquisition
Field Acquisition Integrated
Integrated LiDAR
LiDAR Orthophoto
Orthophoto DEM
DEM DTM/DSM
DTM/DSM 3D Mapping
3D Mapping Topographic
Topographic Infrared
Infrared Feature Extraction
Feature Extraction BIM
BIM Transportation
Transportation Water
Water power
power 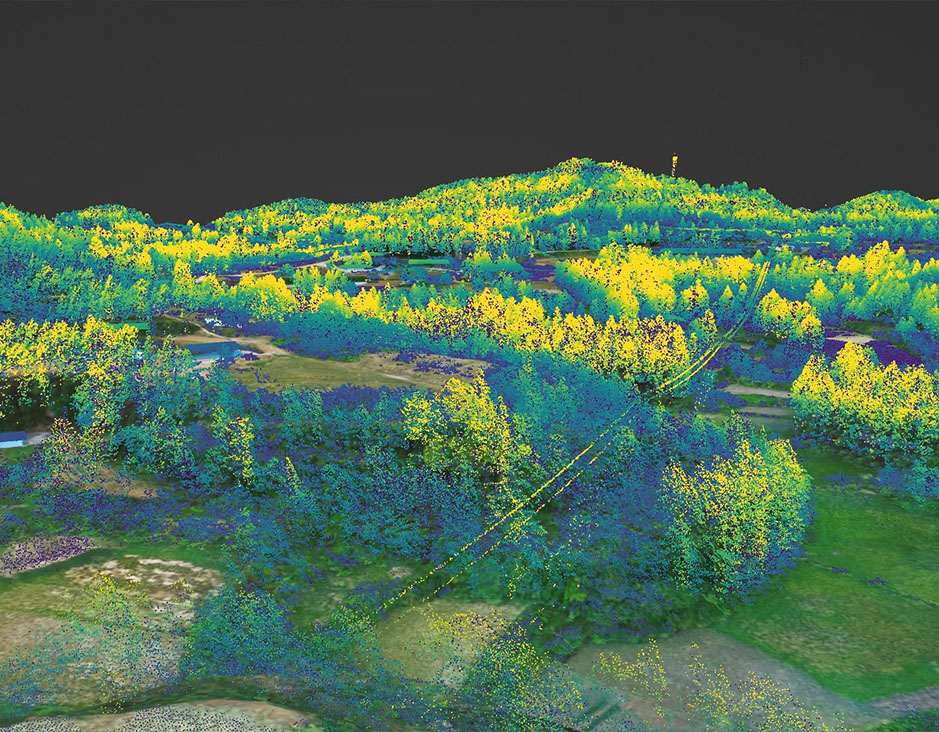 Forestry
Forestry Agriculture
Agriculture Mines & Quarries
Mines & Quarries Heritage Buildings
Heritage Buildings About feiyan
About feiyan Recognition
Recognition Cases
Cases